- Clinical Study
- Clinical Outcomes of COVID-19 Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Population-Based Study in Korea
-
Ji Hong You, Sang Ah Lee, Sung-Youn Chun, Sun Ok Song, Byung-Wan Lee, Dae Jung Kim, Edward J. Boyko
-
Endocrinol Metab. 2020;35(4):901-908. Published online December 10, 2020
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.787
-
-
6,845
View
-
232
Download
-
16
Web of Science
-
20
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF Supplementary Material Supplementary Material PubReader PubReader  ePub ePub
- Background
The aim of this study was to evaluate clinical outcomes in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) positive patients with type 2 diabetes compared to those without diabetes in Korea.
Methods
We extracted claims data for patients diagnosed with COVID-19 from the National Health Insurance Service database in Korea from January 20, 2020 to March 31, 2020. We followed up this cohort until death from COVID-19 or discharge from hospital.
Results
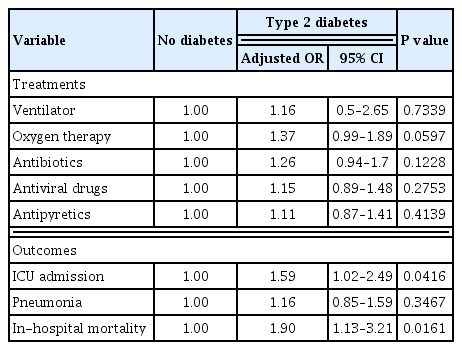
A total of 5,473 patients diagnosed with COVID-19 were analyzed, including 495 with type 2 diabetes and 4,978 without diabetes. Patients with type 2 diabetes were more likely to be treated in the intensive care unit (ICU) (P<0.0001). The incidence of inhospital mortality was higher in patients with type 2 diabetes (P<0.0001). After adjustment for age, sex, insurance status, and comorbidities, odds of ICU admission (adjusted odds ratio [OR], 1.59; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.02 to 2.49; P=0.0416) and in-hospital mortality (adjusted OR, 1.90; 95% CI, 1.13 to 3.21; P=0.0161) among patients with COVID-19 infection were significantly higher in those with type 2 diabetes. However, there was no significant difference between patients with and without type 2 diabetes in ventilator, oxygen therapy, antibiotics, antiviral drugs, antipyretics, and the incidence of pneumonia after adjustment.
Conclusion
COVID-19 positive patients with type 2 diabetes had poorer clinical outcomes with higher risk of ICU admission and in-hospital mortality than those without diabetes. Therefore, medical providers need to consider this more serious clinical course when planning and delivering care to type 2 diabetes patients with COVID-19 infection.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Reasons for Hospitalization Among Australians With Type 1 or Type 2 Diabetes and COVID-19
Dunya Tomic, Jonathan E. Shaw, Dianna J. Magliano
Canadian Journal of Diabetes.2024; 48(1): 53. CrossRef - Predictors of COVID-19 outcome in type 2 diabetes mellitus: a hospital-based study
Amira M. Elsayed, Mohamad S. Elsayed, Ahmed E. Mansour, Ahmed W. Mahedy, Eman M. Araby, Maha H. Morsy, Rasha O. Abd Elmoniem
The Egyptian Journal of Internal Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Diabetes Mellitus and Pneumococcal Pneumonia
Catia Cilloniz, Antoni Torres
Diagnostics.2024; 14(8): 859. CrossRef - Risk for Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus after COVID-19 among Korean Adults: A Nationwide Matched Cohort Study
Jong Han Choi, Kyoung Min Kim, Keeho Song, Gi Hyeon Seo
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(2): 245. CrossRef - The Intersection of COVID-19 and Metabolic-Associated Fatty Liver Disease: An Overview of the Current Evidence
Mykhailo Buchynskyi, Iryna Kamyshna, Valentyn Oksenych, Nataliia Zavidniuk, Aleksandr Kamyshnyi
Viruses.2023; 15(5): 1072. CrossRef - Risk phenotypes of diabetes and association with COVID-19 severity and death: an update of a living systematic review and meta-analysis
Sabrina Schlesinger, Alexander Lang, Nikoletta Christodoulou, Philipp Linnerz, Kalliopi Pafili, Oliver Kuss, Christian Herder, Manuela Neuenschwander, Janett Barbaresko, Michael Roden
Diabetologia.2023; 66(8): 1395. CrossRef - Diabetes and deaths of COVID-19 patients: Systematic review of meta-analyses
Aakriti Garg, Mahesh Kumar Posa, Anoop Kumar
Health Sciences Review.2023; 7: 100099. CrossRef - Cardiometabolic Risk Factors and COVID-19 Outcomes in the Asia-Pacific Region: A Systematic Review, Meta-analysis and Meta-regression of 84,011 Patients
Ru Ying Fong, Annie Lee, Fei Gao, Jonathan Jiunn Liang Yap, Khung Keong Yeo
Journal of Asian Pacific Society of Cardiology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Pituitary Diseases and COVID-19 Outcomes in South Korea: A Nationwide Cohort Study
Jeonghoon Ha, Kyoung Min Kim, Dong-Jun Lim, Keeho Song, Gi Hyeon Seo
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2023; 12(14): 4799. CrossRef - Factors influencing the severity of COVID-19 course for patients with diabetes mellitus in tashkent: a retrospective cohort study
A. V. Alieva, A. A. Djalilov, F. A. Khaydarova, A. V. Alimov, D. Z. Khalilova, V. A. Talenova, N. U. Alimova, M. D. Aripova, A. S. Sadikova
Obesity and metabolism.2023; 20(2): 92. CrossRef - Genetic Predictors of Comorbid Course of COVID-19 and MAFLD: A Comprehensive Analysis
Mykhailo Buchynskyi, Valentyn Oksenych, Iryna Kamyshna, Sandor G. Vari, Aleksandr Kamyshnyi
Viruses.2023; 15(8): 1724. CrossRef - Anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibody levels predict outcome in COVID-19 patients with type 2 diabetes: a prospective cohort study
Sylvia Mink, Christoph H. Saely, Andreas Leiherer, Matthias Frick, Thomas Plattner, Heinz Drexel, Peter Fraunberger
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Two years of SARS-CoV-2 infection (2019–2021): structural biology, vaccination, and current global situation
Waqar Ahmad, Khadija Shabbiri
The Egyptian Journal of Internal Medicine.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Baseline haemoglobin A1c and the risk of COVID‐19 hospitalization among patients with diabetes in the INSIGHT Clinical Research Network
Jea Young Min, Nicholas Williams, Will Simmons, Samprit Banerjee, Fei Wang, Yongkang Zhang, April B. Reese, Alvin I. Mushlin, James H. Flory
Diabetic Medicine.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The Role of Diabetes and Hyperglycemia on COVID-19 Infection Course—A Narrative Review
Evangelia Tzeravini, Eleftherios Stratigakos, Chris Siafarikas, Anastasios Tentolouris, Nikolaos Tentolouris
Frontiers in Clinical Diabetes and Healthcare.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus on the Incidence and Outcomes of COVID-19 Needing Hospital Admission According to Sex: Retrospective Cohort Study Using Hospital Discharge Data in Spain, Year 2020
Jose M. de Miguel-Yanes, Rodrigo Jimenez-Garcia, Javier de Miguel-Diez, Valentin Hernández-Barrera, David Carabantes-Alarcon, Jose J. Zamorano-Leon, Ricardo Omaña-Palanco, Ana Lopez-de-Andres
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2022; 11(9): 2654. CrossRef - The burden and risks of emerging complications of diabetes mellitus
Dunya Tomic, Jonathan E. Shaw, Dianna J. Magliano
Nature Reviews Endocrinology.2022; 18(9): 525. CrossRef - A Comprehensive Analysis of Chinese, Japanese, Korean, US-PIMA Indian, and Trinidadian Screening Scores for Diabetes Risk Assessment and Prediction
Norma Latif Fitriyani, Muhammad Syafrudin, Siti Maghfirotul Ulyah, Ganjar Alfian, Syifa Latif Qolbiyani, Muhammad Anshari
Mathematics.2022; 10(21): 4027. CrossRef - New-Onset Diabetes Mellitus Presenting As Diabetic Ketoacidosis in Patients With COVID-19: A Case Series
Aysha Sarwani, Mahmood Al Saeed, Husain Taha, Rawdha M Al Fardan
Cureus.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - The management of type 2 diabetes before, during and after Covid-19 infection: what is the evidence?
Leszek Czupryniak, Dror Dicker, Roger Lehmann, Martin Prázný, Guntram Schernthaner
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef
- Clinical Study
- Correlation of Glypican-4 Level with Basal Active Glucagon-Like
Peptide 1 Level in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
-
Sang Ah Lee, Gwanpyo Koh, Suk Ju Cho, So-Yeon Yoo, Sang Ouk Chin
-
Endocrinol Metab. 2016;31(3):439-445. Published online September 26, 2016
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2016.31.3.439
-
-
4,040
View
-
41
Download
-
8
Web of Science
-
7
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF Supplementary Material Supplementary Material PubReader PubReader
- Background
Previous studies have reported that glypican-4 (GPC4) regulates insulin
signaling by interacting with insulin receptor and through adipocyte
differentiation. However, GPC4 has not been studied with regard to its
effects on clinical factors in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
(T2DM). We aimed to identify factors associated with GPC4 level in T2DM. MethodsBetween January 2010 and December 2013, we selected 152 subjects with T2DM
and collected serum and plasma into tubes pretreated with aprotinin and
dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor to preserve active gastric inhibitory
polypeptide (GIP) and glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1). GPC4, active GLP-1,
active GIP, and other factors were measured in these plasma samples. We
performed a linear regression analysis to identify factors associated with
GPC4 level. ResultsThe subjects had a mean age of 58.1 years, were mildly obese (mean body mass
index [BMI], 26.1 kg/m2), had T2DM of long-duration (mean, 101.3
months), glycated hemoglobin 7.5%, low insulin secretion, and low insulin
resistance (mean homeostatic model assessment of insulin resistance
[HOMA-IR], 1.2). Their mean GPC4 was 2.0±0.2 ng/mL. In multivariate
analysis, GPC4 was independently associated with age (β=0.224,
P=0.009), and levels of active GLP-1 (β=0.171,
P=0.049) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST;
β=–0.176, P=0.043) after being adjusted for
other clinical factors. ConclusionGPC4 was independently associated with age, active GLP-1, and AST in T2DM
patients, but was not associated with HOMA-IR and BMI, which are well known
factors related to GPC4. Further study is needed to identify the mechanisms
of the association between GPC4 and basal active GLP-1 levels.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - How Reliable are Commercially Available Glypican4 ELISA
Kits?
Joseph P. Buhl, Antje Garten, Jürgen Kratzsch, Wieland Kiess, Melanie Penke
Experimental and Clinical Endocrinology & Diabetes.2022; 130(02): 110. CrossRef - Serum glypican-4 is associated with the 10-year clinical outcome of patients with peripheral artery disease
Axel Muendlein, Christine Heinzle, Andreas Leiherer, Kathrin Geiger, Eva Maria Brandtner, Stella Gaenger, Peter Fraunberger, Christoph H. Saely, Heinz Drexel
International Journal of Cardiology.2022; 369: 54. CrossRef - Berberine activates the β-catenin/TCF4 signaling pathway by down-regulating miR-106b to promote GLP-1 production by intestinal L cells
Jiao Wang, Li-Rui Wei, Yan-Ling Liu, Cheng-Zhi Ding, Feng Guo, Jiao Wang, Qian Qin, Feng-Jiao Huang, Ying Xin, Sheng-Nan Ma, Qiu-Ran Zhai, Shou-Jun Wang, Gui-Jun Qin
European Journal of Pharmacology.2021; 911: 174482. CrossRef - Increased Glypican-4 Levels Are Associated with Obesity in Adolescents
Huseyin Dag, Nevin Cetin Dag, Okan Dikker
Iranian Journal of Pediatrics.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Serum glypican 4 level in obese children and its relation to degree of obesity
Chutima Leelalertlauw, Manassawee Korwutthikulrangsri, Pat Mahachoklertwattana, Suwannee Chanprasertyothin, Patcharin Khlairit, Sarunyu Pongratanakul, Preamrudee Poomthavorn
Clinical Endocrinology.2017; 87(6): 689. CrossRef - Articles inEndocrinology and Metabolismin 2016
Won-Young Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2017; 32(1): 62. CrossRef - Efficacy and Safety of Single‐ or Double‐Drug Antidiabetic Regimens in the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Network Meta‐Analysis
Xi‐Ling Yang, Mi‐Ma Duo‐Ji, Zi‐Wen Long
Journal of Cellular Biochemistry.2017; 118(12): 4536. CrossRef
- Obesity and Metabolism
- Apolipoprotein B Is Related to Metabolic Syndrome Independently of Low Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
-
Younghyup Lim, Soyeon Yoo, Sang Ah Lee, Sang Ouk Chin, Dahee Heo, Jae Cheol Moon, Shinhang Moon, Kiyoung Boo, Seong Taeg Kim, Hye Mi Seo, Hyeyoung Jwa, Gwanpyo Koh
-
Endocrinol Metab. 2015;30(2):208-215. Published online June 30, 2015
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2015.30.2.208
-
-
4,540
View
-
46
Download
-
19
Web of Science
-
21
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader
- Background
Increased low density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) level and the presence of metabolic syndrome (MetS) are important risk factors for cardiovascular disease (CVD) in type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). Recent studies demonstrated apolipoprotein B (apoB), a protein mainly located in LDL-C, was an independent predictor of the development of CVD especially in patients with T2DM. The aim of this study was to investigate the relationship between apoB and MetS in T2DM patients. MethodsWe analyzed 912 patients with T2DM. Fasting blood samples were taken for glycated hemoglobin, high-sensitivity C-reactive protein, total cholesterol, triglyceride (TG), high density lipoprotein cholesterol, LDL-C, and apoB. MetS was defined by the modified National Cholesterol Education Program Adult Treatment Panel III criteria. We performed a hierarchical regression analysis with apoB as the dependent variable. Age, sex, the number of components of MetS and LDL-C were entered at model 1, the use of lipid-lowering medications at model 2, and the individual components of MetS were added at model 3. ResultsSeventy percent of total subjects had MetS. ApoB level was higher in subjects with than those without MetS (104.5±53.3 mg/dL vs. 87.7±33.7 mg/dL, P<0.01) even after adjusting for LDL-C. ApoB and LDL-C were positively correlated to the number of MetS components. The hierarchical regression analysis showed that the increasing number of MetS components was associated with higher level of apoB at step 1 and step 2 (β=0.120, P<0.001 and β=0.110, P<0.001, respectively). At step 3, TG (β=0.116, P<0.001) and systolic blood pressure (β=0.099, P<0.05) were found to significantly contribute to apoB. ConclusionIn patients with T2DM, apoB is significantly related to MetS independently of LDL-C level. Of the components of MetS, TG, and systolic blood pressure appeared to be determinants of apoB.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - ApoB100 and Atherosclerosis: What’s New in the 21st Century?
Dimitris Kounatidis, Natalia G. Vallianou, Aikaterini Poulaki, Angelos Evangelopoulos, Fotis Panagopoulos, Theodora Stratigou, Eleni Geladari, Irene Karampela, Maria Dalamaga
Metabolites.2024; 14(2): 123. CrossRef - Association of apolipoproteins and lipoprotein(a) with metabolic syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Juan R. Ulloque-Badaracco, Ali Al-kassab-Córdova, Enrique A. Hernandez-Bustamante, Esteban A. Alarcon-Braga, Miguel Huayta-Cortez, Ximena L. Carballo-Tello, Rosa A. Seminario-Amez, Percy Herrera-Añazco, Vicente A. Benites-Zapata
Lipids in Health and Disease.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Current Data and New Insights into the Genetic Factors of Atherogenic Dyslipidemia Associated with Metabolic Syndrome
Lăcramioara Ionela Butnariu, Eusebiu Vlad Gorduza, Elena Țarcă, Monica-Cristina Pânzaru, Setalia Popa, Simona Stoleriu, Vasile Valeriu Lupu, Ancuta Lupu, Elena Cojocaru, Laura Mihaela Trandafir, Ștefana Maria Moisă, Andreea Florea, Laura Stătescu, Minerva
Diagnostics.2023; 13(14): 2348. CrossRef - Apolipoprotein B compared with low-density lipoprotein cholesterol in the atherosclerotic cardiovascular diseases risk assessment
Federica Galimberti, Manuela Casula, Elena Olmastroni
Pharmacological Research.2023; 195: 106873. CrossRef - Circulating lipids and breast cancer prognosis in the Malmö diet and cancer study
Sixten Harborg, Thomas P. Ahern, Maria Feldt, Ann H. Rosendahl, Deirdre Cronin-Fenton, Olle Melander, Signe Borgquist
Breast Cancer Research and Treatment.2022; 191(3): 611. CrossRef - Metabolic disorders in patients with impaired glucose tolerance, with or without underlying ischaemic heart disease
Milena Brkić, Danijel Đekić, Jelena Jovanić, Goran Topić, Aleksandra Grbić, Tatjana Šutilović
Scripta Medica.2022; 53(3): 175. CrossRef - Genetics of Cholesterol-Related Genes in Metabolic Syndrome: A Review of Current Evidence
Sok Kuan Wong, Fitri Fareez Ramli, Adli Ali, Nurul ‘Izzah Ibrahim
Biomedicines.2022; 10(12): 3239. CrossRef - Prevalence of ApoB100 rs693 gene polymorphism in metabolic syndrome among female students at King Abdulaziz University
Rana A. Alghamdi, Maryam H. Al-Zahrani, Maha J. Balgoon, Nuha A. Alkhattabi
Saudi Journal of Biological Sciences.2021; 28(6): 3249. CrossRef - Local ablation of gastric cancer by reconstituted apolipoprotein B lipoparticles carrying epigenetic drugs
Chia-Lung Yang, Ying-Jui Chao, Hao-Chen Wang, Ya-Chin Hou, Caleb Gonshen Chen, Chia-Ching Chang, Yan-Shen Shan
Nanomedicine: Nanotechnology, Biology and Medicine.2021; 37: 102450. CrossRef - Cardiovascular Biomarkers of Obesity and Overlap With Cardiometabolic Dysfunction
Emily S. Lau, Samantha M. Paniagua, Shahrooz Zarbafian, Udo Hoffman, Michelle T. Long, Shih‐Jen Hwang, Paul Courchesne, Chen Yao, Jiantao Ma, Martin G. Larson, Daniel Levy, Ravi V. Shah, Jennifer E. Ho
Journal of the American Heart Association.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - The association of ecg TV1>TV6 phenomenon as electrophysiological sign of metabolic myocardial disorders with risk factors for ischemic heart disease in the population of 25–44 years
N. A. Kuzminykh, L. V. Shcherbakova, V. S. Shramko, D. V. Denisova, Yu. I. Ragino
Ateroscleroz.2021; 17(2): 22. CrossRef - Regulation of Apolipoprotein B by Natural Products and Nutraceuticals: A Comprehensive Review
Mohammad Bagherniya, Thomas P. Johnston, Amirhossein Sahebkar
Current Medicinal Chemistry.2021; 28(7): 1363. CrossRef - Apolipoprotein B and non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol reveal a high atherogenicity in individuals with type 2 diabetes and controlled low-density lipoprotein-cholesterol
Liliana Fonseca, Sílvia Paredes, Helena Ramos, José Carlos Oliveira, Isabel Palma
Lipids in Health and Disease.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Menopause-Associated Lipid Metabolic Disorders and Foods Beneficial for Postmenopausal Women
Seong-Hee Ko, Hyun-Sook Kim
Nutrients.2020; 12(1): 202. CrossRef - Lipoprotein A, combined with alanine aminotransferase and aspartate aminotransferase, contributes to predicting the occurrence of NASH: a cross-sectional study
Yu Zhang, He He, Yu-Ping Zeng, Li-Dan Yang, Dan Jia, Zhen-Mei An, Wei-Guo Jia
Lipids in Health and Disease.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Novel and traditional lipid profiles in Metabolic Syndrome reveal a high atherogenicity
Sílvia Paredes, Liliana Fonseca, Laura Ribeiro, Helena Ramos, José Carlos Oliveira, Isabel Palma
Scientific Reports.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Serum apolipoprotein B is associated with increased risk of metabolic syndrome among middle‐aged and elderly Chinese: A cross‐sectional and prospective cohort study
Rui Du, Xueyan Wu, Kui Peng, Lin Lin, Mian Li, Yu Xu, Min Xu, Yuhong Chen, Donghui Li, Jieli Lu, Yufang Bi, Weiqing Wang, Guang Ning
Journal of Diabetes.2019; 11(9): 752. CrossRef - The role of metabolism disorders, inflammation, myocardial injury in development chronic heart failure in metabolic syndrome patients
A. P. Roytman, T. A. Fedorova, E. A. Ivanova, A. V. Bugrov, V. V. Dolgov
Laboratornaya sluzhba.2018; 7(4): 5. CrossRef - Serum apoB levels independently predict the development of non‐alcoholic fatty liver disease: A 7‐year prospective study
Jinghua Wang, Wanlin Zhu, Shujun Huang, Lei Xu, Min Miao, Chenjiao Wu, Chaohui Yu, Youming Li, Chengfu Xu
Liver International.2017; 37(8): 1202. CrossRef - Comprehensive assessment of lipoprotein subfraction profiles according to glucose metabolism status, and association with insulin resistance in subjects with early-stage impaired glucose metabolism
Jie-Eun Lee, Se Hee Min, Dong-Hwa Lee, Tae Jung Oh, Kyoung Min Kim, Jae Hoon Moon, Sung Hee Choi, Kyong Soo Park, Hak Chul Jang, Soo Lim
International Journal of Cardiology.2016; 225: 327. CrossRef - Association of Serum Apolipoprotein B with the Increased Risk of Diabetes in Korean Men
Hyo Hee Lim, Oh Yoen Kim
Clinical Nutrition Research.2016; 5(3): 204. CrossRef
- A Case of Familial Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia Type 1 with a Novel Mutation in the MEN1 Gene.
-
Min Jung Kim, Eun Hee Kim, Mi Seon Shin, Joo Hui Kim, Hee Kyung Na, Seong Joon Park, Sang Ah Lee, Eun Hee Koh, Woo Je Lee, Ki Ho Song, Joong Yeol Park, Ki Up Lee, Gu Hwan Kim, Han Wook Yoo, Min Seon Kim
-
Endocrinol Metab. 2011;26(2):171-176. Published online June 1, 2011
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2011.26.2.171
-
-
1,952
View
-
31
Download
-
2
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1 (MEN1) is an autosomal dominant disorder characterized by the occurrence of multiple tumors in the parathyroid gland, pancreatic islet, and pituitary gland. This condition is caused by mutations of MEN1, a tumor suppressor gene. Thus far, 565 different germline and somatic mutations of the MEN1 gene have been reported. Herein, we describe the case of a 23-year-old woman who suffered from a repetitive loss of consciousness. After workup, the patient was diagnosed with MEN1 with insulinoma, hyperparathyrodism due to parathyroid adenoma, and non-functioning pituitary microadenoma. She underwent a partial parathyroidectomy and distal pancreatectomy. Familial screening of MEN1 revealed that her brother had prolactinoma, hyperparathyroidism, pancreatic gastrinoma and non-functioning adrenal adenoma. Her father had hyperparathyroidism, pancreatic tumor, and adrenal adenoma. Upon genetic analysis of the MEN1 gene, a novel mutation in the MEN1 gene (exon 1, c.251del; p.Ser84LuefsX35) was detected in the patient, as well as her father and brother.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Parathyroid disorder and concomitant thyroid cancer in patients with multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1
Ying Wang, Sheng Cai, He Liu, Rui-Na Zhao, Xing-Jian Lai, Ke Lv, Yu-Xin Jiang, Jian-Chu Li
Medicine.2021; 100(36): e27098. CrossRef - Genetic and Epigenetic Analysis in Korean Patients with Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia Type 1
Yoon Jung Chung, Sena Hwang, Jong Ju Jeong, Sun Yong Song, Se Hoon Kim, Yumie Rhee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2014; 29(3): 270. CrossRef
- A Case of Painful Graves' Disease.
-
Ji Yun Jeong, Tae Yong Kim, Eun Hee Kim, Eui Young Kim, Sang Ah Lee, Ji Hye Yim, Kyung Min Kim, Won Bae Kim, Young Kee Shong
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 2008;23(5):337-341. Published online October 1, 2008
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/jkes.2008.23.5.337
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Graves' disease rarely presents as pain and tenderness of goiter, with only a few cases reported in the literature. We describe a case of painful Graves' disease presenting as 2 episodes of painful goiter.
- A Case of Carcinoma Showing Thymus-Like Differentiation (CASTLE) in the Thyroid.
-
Eun Hee Kim, Ji Yun Jeong, Eui Young Kim, Sang Ah Lee, Kyung Min Kim, Ji Hye Yim, Won Gu Kim, Tae Yong Kim, Sun A Kim, Gyungyup Gong, Young Kee Shong, Won Bae Kim
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 2008;23(4):272-276. Published online August 1, 2008
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/jkes.2008.23.4.272
-
-
1,681
View
-
24
Download
-
2
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Carcinoma Showing Thymus-Like Differentiation (CASTLE) is a very rare malignant neoplasm of the thyroid, and this resembles lymphoepithelioma or squamous cell carcinoma of the thymus. It originates from ectopic thymic tissue or remnants of the branchial pouches. We recently experienced a case of CASTLE in the thyroid gland of a 61-year-old woman. She presented with an asymptomatic mass in the right thyroid gland and she was diagnosed with 'poorly differentiated carcinoma' of the thyroid by fine needle aspiration cytology (FNAC). Total thyroidectomy was performed for both diagnostic and therapeutic purposes. Histologic examination of the resected tumor showed that the tumor was lobulated with expanding fibrous bands, and it was infiltrated by lymphocytes and plasma cells. The tumor cells had oval, large vesicular nuclei and prominent nucleoli, and the immunohistochemical staining was positive for CD5 and bcl-2, so the patient was diagnosed with thyroid CASTLE. We report here on a case of CASTLE in the thyroid gland treated by surgery and external neck radiation therapy.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Intrathyroidal thymic carcinoma exhibiting neuroendocrine differentiation: Case report with cytomorphology, immunocytochemistry, and review of the literature focusing on cytology
Wen‐hao Ren, Kun Dong, Xiao‐zheng Huang, Yan‐li Zhu
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2019; 47(11): 1197. CrossRef - Cytologic Findings of Thyroid Carcinoma Showing Thymus-like Differentiation: A Case Report
Sunhee Chang, Mee Joo, Hanseong Kim
Korean Journal of Pathology.2012; 46(3): 302. CrossRef
- A Case of Diffuse Hemorrhage into the Thyroid Gland after Fine Needle Aspiration, and This was Treated by Arterial Embolization.
-
Eui Young Kim, Jung Min Kim, Eun Hee Kim, Ji Yun Jeong, Sang Ah Lee, Ji Young Choi, Ji Hye Yim, Pil Hyung Lee, Tae Yong Kim, Young Kee Shong, Won Bae Kim
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 2008;23(3):199-203. Published online June 1, 2008
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/jkes.2008.23.3.199
-
-
1,977
View
-
27
Download
-
2
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Although hematoma formation after fine needle aspiration cytology fine needle aspiration cytology (FNAC) is a most common complication and most of these hematomas are self-limiting with minimal pain, a massive intra-thyroidal hemorrhage that produces acute airway obstruction had rarely been reported on.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Characteristics Evaluation of Hobun Pigments according to Shell Types and Calcination
Ju Hyun Park, Sun Myung Lee, Myoung Nam Kim, Jin Young Hong
Economic and Environmental Geology.2023; 56(6): 899. CrossRef - Endovascular treatment of massive hemorrhage arising from inferior thyroid artery after fine needle aspiration of thyroid: a case report
Ho Sig Jang, Yook Kim
BMC Surgery.2021;[Epub] CrossRef
|